
Defence 2024 Current Affairs- Important for all competitive exams
Get the latest updates on Defence-related current affairs in 2024, including exercises and military developments. Stay informed with Minikosh.
Table of Contents
DRDO Successfully Conducts Test of New Generation Ballistic Missile ‘Agni-Prime
DRDO and India’s Strategic Forces Command have Successfully tested Agni-Prime at Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha in April 2024.
About Agni-Prime: It ranges from 1,000 to 2,000 km and has technology advancement from Agni- IV and Agni-V. Its weight is half of the weight of Agni-III, designed for improved maneuverability and precision. It is developed to replace Prithvi-II, Agni-II, Agni-III, and Agni-IV missiles.
Agni Missile Series
These are Developed under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) initiated by Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam in the 1980s.
Medium to intercontinental ballistic missiles.
- Agni-I: 700-1,200 km range
- Agni-II: 2,000-3,000 km range
- Agni-III: 3,500-5,000 km range
- Agni-IV: ~4,000 km range
- Agni-V: Over 7,000 km range
- Agni-P/Agni-Prime: 1,000-2,000 km range
DRDO Founded: 1958, Headquarters– New Delhi, Chairman: Sameer V. Kamat
President’s Standard and Colours Ceremony
In March 2024, President Droupadi Murmu awarded the President’s Standard to 45 Squadron and 221 Squadron, and the President’s Colours to 11 Base Repair Depot and 509 Signal Unit at Air Force Station Hindan.

This was the first instance of four units being honored simultaneously in a single ceremony.
Honouree’s:
- No. 45 ‘Flying Daggers’: First Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) squadron in IAF.
- No. 221 Squadron ‘Valiants’: Key role in the 1999 Kargil conflict.
- 11 Base Repair Depot.
- 509 Signal Unit.
Award recipients: Group Captain M Surendran (45 Squadron), Group Captain Shubhankan (221 Squadron), Air Commodore Ashutosh Vaidya (11 BRD), Group Captain Vivek Sharma (509 SU).
The President highlighted IAF’s bravery in historical conflicts and its role in disaster relief, emphasizing its modernization and strategic significance.
DRDO’s SMART System Success

- On May 1, 2024, DRDO successfully tested the Supersonic Missile-Assisted Release of Torpedo (SMART) system off Odisha’s coast.
- SMART extends the range of lightweight torpedoes, enhancing India’s anti-submarine warfare capabilities.
- Features include a two-stage solid propulsion mechanism, advanced electromechanical actuators, and a precise inertial navigation system.
- Defense Minister Rajnath Singh and DRDO Chairman Dr. Samir V Kamat praised the achievement, noting its strategic importance for the Navy.
India and France’s 7th Joint Military Exercise ‘Shakti’
From May 13 to May 26, 2024, India and France have conducted the 7th Joint Military Exercise ‘Shakti’ in Umroi, Meghalaya. This exercise aimed to enhance joint military capabilities for multi-domain operations, focusing on diverse tactics across air, land, sea, and cyberspace. The previous edition in 2021 was held in Draguignan, France, involving joint operation planning and counter-terrorism. Initiated in 2011, the Shakti exercise strengthens military cooperation and counter-terrorism capabilities between the two nations.
Also Read T20 World Cup 2024 Current Affairs
Drishti-10 Drone: A Versatile Tool for Surveillance and Disaster Management
The Indian Army will receive its first Drishti-10 (Hermes-900 Starliner) drone on June 18. Delivered by Adani Defence Systems using emergency powers from the Defence Ministry, the drone can fly for over 30 hours and cover 2,000 km, ideal for extensive surveillance. It features advanced technology from Israeli firm Elbit, with a tech transfer agreement to support local manufacturing by Adani Defence.
About Hermes-900 Starliner
The Hermes-900 Starliner, from Israel’s Elbit Systems, is a sophisticated UAV designed for intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, and communication relay. It has a 15-meter wingspan and can fly for up to 36 hours at altitudes above 30,000 feet. Launched in the late 2010s, it includes satellite communication, collision avoidance systems, and advanced payloads, suitable for both civil and military airspace. An upgrade of the Hermes-450, it offers increased payload capacity and longer endurance.
Deployment and Operational Strategy
Post-delivery, the drones will be stationed at the Army’s Bhatinda base in Punjab, strategically positioned to monitor the western frontier with Pakistan, enhancing reconnaissance and security operations.
Indian Army and IAF Conduct Joint Exercise in Punjab
The Indian Army’s Kharga Corps, part of the Western Command, and the Indian Air Force combinedly conducted a three-day exercise in Punjab in May 2024, to refine and validate attack helicopter support for mechanized operations in developed terrain. Exercise Gagan Strike-II showcased joint military capabilities by involving Apache and ALH-WSI helicopters, UAVs, and Indian Army special forces to validate their use in supporting ground offensive operations.
Ground leaders employed aerial assets such as drones to improve situational awareness and neutralize both moving and stationary targets. The drill facilitated smooth integration of ground and aerial resources, enabling Western Command formations and units to execute joint operations efficiently. The exercise confirmed the operational proficiency and coordination of both forces.
India Receives Initial Shipment of Igla-S Man-Portable Air Defence Systems (MANPADS)
The Indian Army has received its first batch of 24 Russia-made Igla-S MANPADS and 100 missiles, part of a larger deal for 120 launchers and 400 missiles, aimed at boosting VSHORAD capabilities in mountainous northern regions. The remaining systems will be produced in India under a Transfer of Technology (ToT) agreement. The Igla-S system, capable of targeting low-flying aircraft, cruise missiles, and drones, includes the 9M342 missile, the 9P522 launch mechanism, the 9V866-2 mobile testing station, and the 9F719-2 testing set.
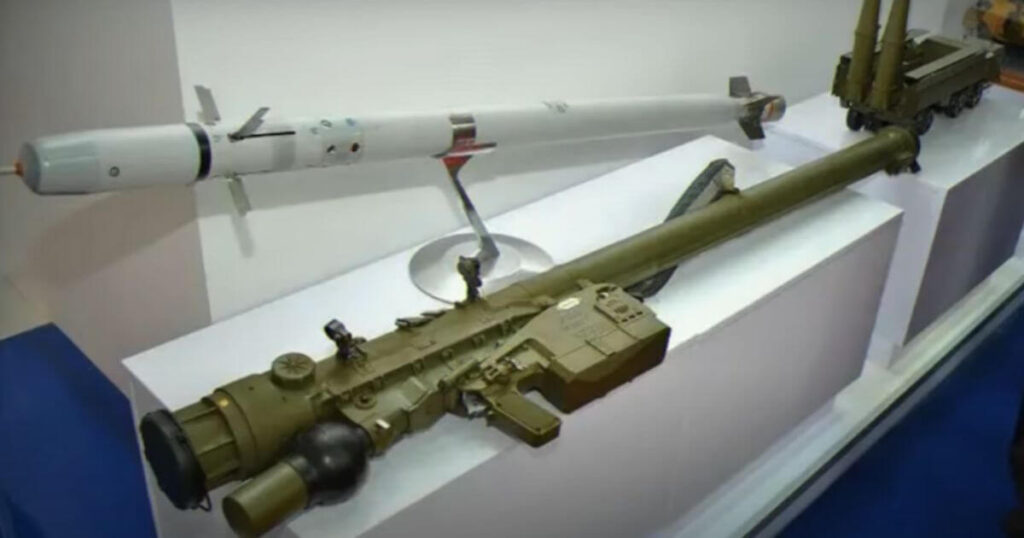

After meeting the current needs, the Indian Army intends to upgrade the older Igla systems with advanced laser-beam riding and infrared VSHORADS. The DRDO has shown progress in this initiative by recently conducting two flight tests of locally developed VSHORADS missiles.
Read about IPL 2024 current affairs
Indian Navy Undertakes ‘Poorvi Leher’ Major Drill to Assess Maritime Readinesss
The Indian Navy carried out the ‘Poorvi Leher’ mega exercise along the East Coast to validate procedures and assess readiness for maritime security challenges. The drill included ships, submarines, aircraft, and special naval forces. This exercise is conducted in multiple phases, it included realistic combat training and live-fire drills, demonstrating the Navy’s precision in delivering ordnance on target.
The Navy maintained near-continuous maritime domain awareness by operating aircraft from various locations, showcasing effective monitoring and response capabilities. The exercise involved the Indian Air Force, Andaman and Nicobar Command, and the Coast Guard, highlighting strong interoperability among armed forces for coordinated operations.
Enhancing Operational Readiness-‘Poorvi Leher’ improved forces’ readiness to tackle maritime challenges under realistic conditions, reinforcing the Navy’s commitment to safeguarding maritime interests.
Testing Maritime Security Capabilities- Conducted along the East Coast, the exercise underscored the Navy’s dedication to enhancing maritime security and preparedness for regional threats through joint operations and scenario simulations.
Coastal Security Drill “Sagar Kavach 2024” Held in Lakshadweep Islands
The two-day coastal security exercise, Sagar Kavach 01/24, was held off the Lakshadweep Islands from April 1-2, 2024. In this the Indian Navy, Indian Coast Guard, Marine Police, Fisheries, Customs, and other security agencies were involved.
The key objectives were:
- To Validate the coastal security mechanism against asymmetric sea threats.
- To improve preparedness, response, surveillance, and coordination among maritime security agencies.
The significance of this exercise was
- Strengthens coastal security.
- Identifies gaps and areas for improvement.
- Ensures maritime agencies are prepared for potential threats.
- Enhances cooperation and coordination among stakeholders.
DRDO Creates World’s Lightest Bulletproof jacket
A division of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully created the country’s lightest bulletproof jacket, designed to protect against the highest threat level 6, according to an official statement. The Ministry of Defence noted that this jacket employs an innovative design approach utilizing novel materials and new manufacturing processes.
Key Features of the lightest bulletproof jacket:
- Protection against 7.62 x 54 R API ammunition (Level 6 of BIS 17051)
- Innovative design with new materials and processes
- Front Hard Armour Panel (HAP) withstands multiple hits from sniper rounds
- Ergonomic design for enhanced wearability and comfort
- Areal density of ICW HAP < 40 kg/m2, Standalone HAP < 43 kg/m2
- Tested at Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL), Chandigarh Significance:
- Enhanced protection for security personnel
- Improves mobility and comfort
- Showcases DRDO’s advanced capabilities About:
- Developed by DRDO-DMSRDE, Kanpur
- Highest threat level 6 protection (BIS 17051)
- Tested against 7.62 x 54 R API ammunition
- Testing facility: Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL), Chandigarh
DMSRDE, Kanpur has successfully developed indigenous light weight Bullet Proof Jacket( BPJ) for protection against highest threat level 6 of BIS. This is the first of its kind in monolithic ceramic which can stop 6 7.62×54 API bullets@DefenceMinIndia @SpokespersonMoD pic.twitter.com/v8O43kf8hC
— DRDO (@DRDO_India) April 23, 2024
Cabinet ministers of India 2024
The Oron: AI-Driven Sentinel of the Skies Defends Against Missile Attack
An advanced AI aircraft named ‘The Oron,’ also known as Mars 2, acted as Israel’s protector during a missile and drone attack on April 13. Valued at approximately £800 million, this cutting-edge stealth aircraft demonstrated its swift and powerful defense capabilities.
The Oron is more than just an aircraft; it’s a technological marvel equipped with advanced sensors and systems that enable it to detect threats with unmatched precision. During the recent attack, it played a crucial role in identifying incoming missiles from Iran, allowing Israel to quickly launch countermeasures.
The integration of AI-powered aircraft like the Oron is part of a broader movement towards autonomous systems in defense. Utilizing artificial intelligence in military aircraft not only enhances real-time threat detection and response but also aids in intelligence gathering and reconnaissance missions. Many of these aircraft are designed with a network-centric approach, allowing them to coordinate with other defense systems to provide comprehensive security.
Indian Air Force Trials Airdrop of BHISHM Portable Hospital in Agra
The Indian Air Force recently in may tested the BHISHM portable hospital in Agra, a key element of “Project BHISHM” designed to deliver rapid, comprehensive medical aid during emergencies. These portable units can treat up to 200 casualties, highlighting quick response and extensive care.
Features : Equipped with modern technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics, the BHISHM portable hospital ensures efficient on-site medical management. It includes 72 transportable components that can be moved by hand, bicycle, or potentially drones, allowing for versatile deployment in various situations. These hospitals are durable, waterproof, and lightweight, allowing for rapid setup in about 12 minutes, crucial during large-scale emergencies or disasters.
Successfully deployed during a major event in Ayodhya, these portable hospitals demonstrated swift setup and effective operation. The recent tests and future deployments highlight their potential to enhance disaster and emergency response, ensuring timely medical assistance wherever needed.
National Organizations and their HQ
Dosti-16′ Joint Exercise by India, Maldives, and Sri Lanka Held in the Maldives
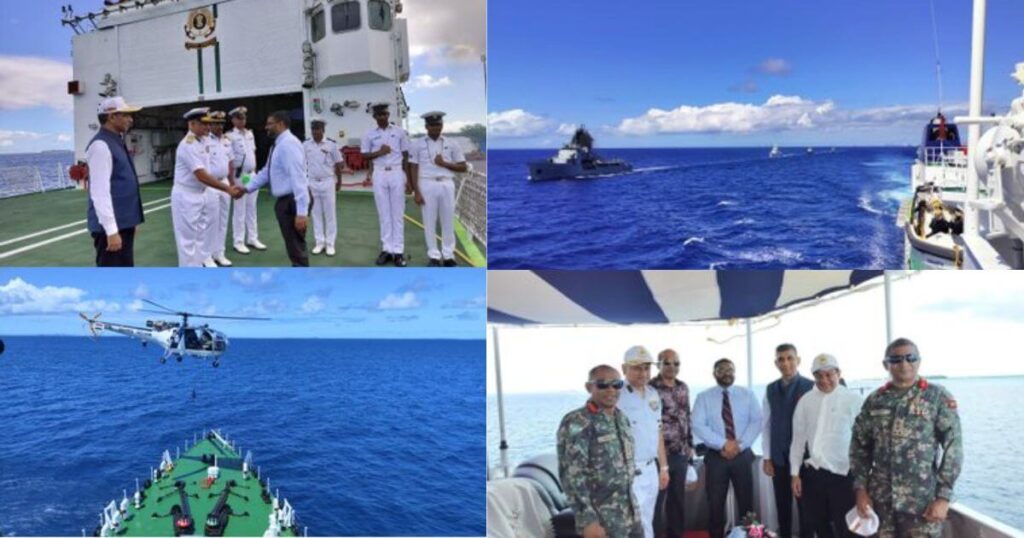

The Indian Mission in Maldives referred to the 16th edition of the India-Maldives-Sri Lanka trilateral exercise ‘Dosti’ as a collaborative effort aimed to enhance cooperation, strengthen operational capabilities, and develop interoperability. Activities included interdiction operations, search and rescue missions, surveillance, and communication drills. The exercise underscored regional cooperation in various areas including search and rescue, countering piracy, and humanitarian assistance. Important officials attended the inauguration ceremony, and efforts were made to foster cooperation among maritime neighbors. Started in 1992, ‘Dosti’ has evolved to include Sri Lanka and Bangladesh as an observer, expanding its scope.
Helen Mary Roberts: First Woman Brigadier from Minority Community in Pakistan Army
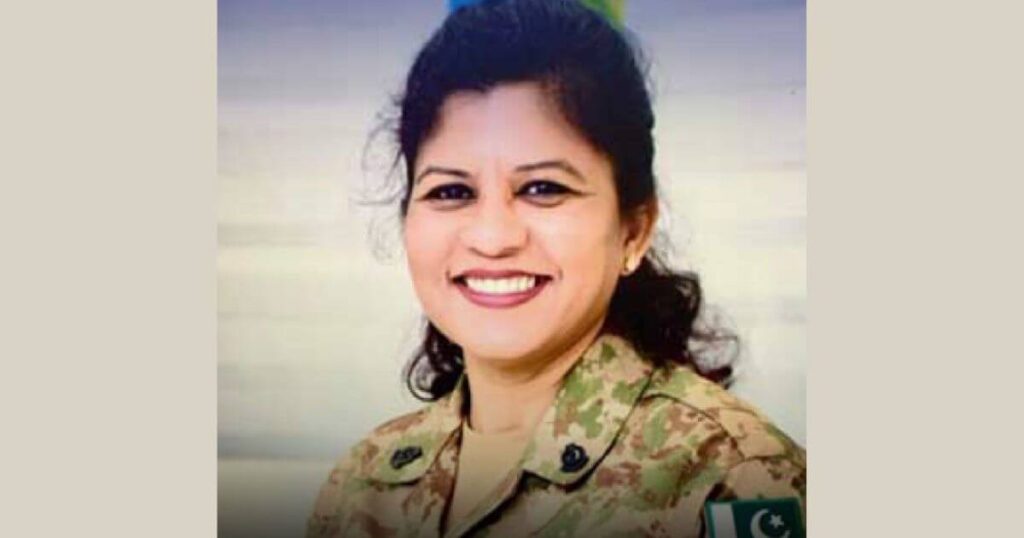

Dr. Helen Mary Roberts, a Christian, achieves historic milestone as Pakistan’s first one-star officer, amid rising concerns over minority rights. The promotion highlights merit-based advancements in the military and offers hope amidst religious tensions. Dr. Roberts, a senior pathologist with 26 years of service, represents national diversity within the Pakistan Army. Her elevation follows Major-General Nigar Johar’s breakthrough as the first female lieutenant general in 2020. In Pakistan, Muslims comprise 96.47%, with minorities including Hindus (2.14%) and Christians (1.27%).
Udbhav Initiative to Revive Ancient Military Traditions
Hon’ble Defence Minister Rajnath Singh and senior military officials inaugurated “Project UDBHAV” at the Indian Military Heritage Festival in May 2024. This joint effort between the Indian Army and the United Services Institution of India (USI) seeks to merge India’s rich military heritage with modern strategic approaches. Project UDBHAV, meaning “origin” or “genesis,” aims to integrate India’s extensive military knowledge from historical texts into modern defense strategies, enhancing contemporary warfare techniques.
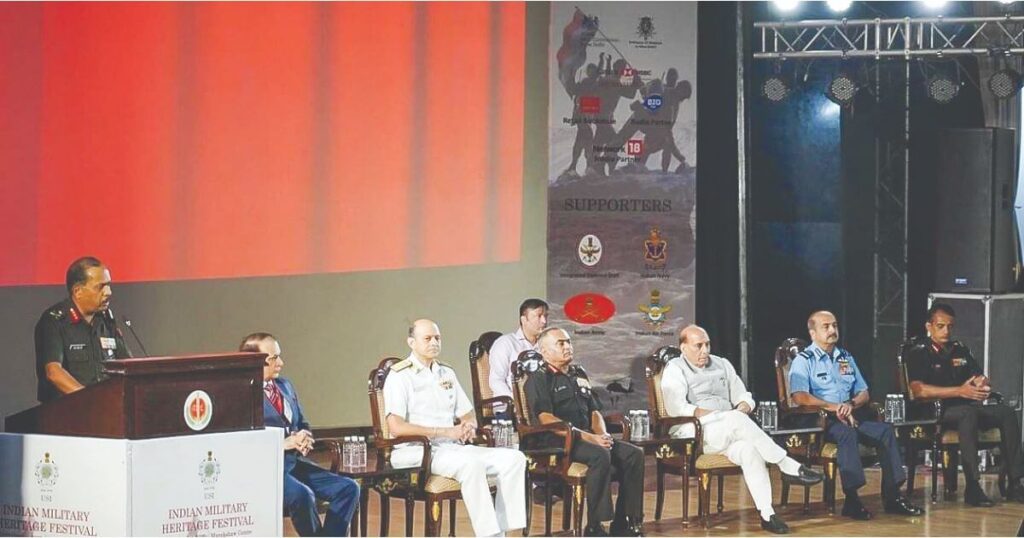

Project UDBHAV
- Launched by the Government of India under the Samagra Shiksha Scheme.
- Aims to transform government schools into vibrant learning environments.
- Focuses on improving pedagogy and infrastructure to create inclusive, child-friendly schools.
- Categorizes schools into foundational, middle, and senior levels.
- Emphasizes better teaching methods, digital learning tools, and community involvement.
- Promotes activity-based learning to foster creativity and critical thinking in students.
About Indian Military Heritage Festival – An annual event celebrating India’s military history with vintage vehicle displays, historical battle reenactments, military band performances, and traditional martial arts demonstrations. It also provides a platform for soldiers to share experiences, enriching public understanding of military life and history.
Japan and the US to Jointly Develop Hypersonic Missile Interceptors by the 2030s
Japan and the US have agreed to jointly develop interceptors for hypersonic missiles, formalizing the deal with a contract exceeding $3 billion. The decision emerged from an August meeting at Camp David, which also included South Korea.
Japan-United States Military Collaboration
- Treaty of Mutual Cooperation and Security (1960): This agreement strengthens regional security and forms the basis of US-Japan military cooperation.
- Post-WWII Limits: Japan’s pacifist constitution initially limited its military capabilities.
- Self-Defense Forces (SDF): Since 1954, the SDF has closely worked with US forces despite constitutional restrictions.
- Increased Cooperation: Growing threats from China and North Korea have bolstered US-Japan military ties.
- Revised Defense Guidelines (2015): These allow Japan a more active role in global peacekeeping, enhancing the partnership.
- Key Installations: US military bases in Okinawa are vital for regional security.
- Joint Drills: Exercises like Keen Sword showcase the strong cooperation between Japanese and US forces.
- Technology Sharing: The partnership involves sharing advanced technologies, including missile defense systems and next-generation stealth aircraft.
For 2023, Japan’s defense budget hit a record ¥6.8 trillion, a 20% increase, reflecting a more assertive defense stance. Recent reviews emphasize improving missile defense and cyber warfare capabilities. In response to threats from North Korea and China, Japan is developing counterstrike abilities and aims to double defense spending to 2% of GDP by 2027, incorporating technologies like drones and AI.
Important Operations and Missions 2024| Current affairs on operations 2024 (Part-1)


Very nice
Thank you 😊