Indian Organizations and their headquarters| Current Affairs 2026
Discover the headquarters and objectives of major Indian organizations, in this informative blog. Increase your GK and stay updated with current affairs 2026.
Table of Contents
Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India whose primary function is to manage and govern the financial system of the country. It is a statutory body established in the year 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The central bank regulates the issue and supply of the Indian rupee. It also looks after the central government’s money. The central bank plays the role of the bankers’ bank and regulates the banking sector. It also plays an important role in India’s development story by supporting the government in its developmental projects and policies.
The head office of the RBI, in Kolkata when the bank was established, was shifted to Mumbai in 1937. Originally, the bank was privately owned. However, after Independence, it was nationalized in 1949 and is now fully owned by the Government of India.
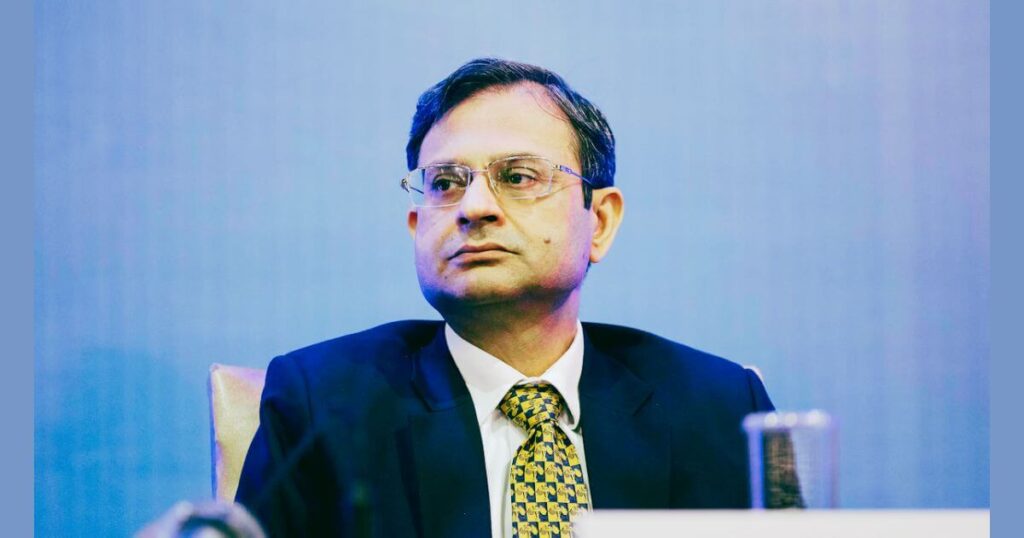

Current Governor of RBI is Sanjay Malhotra.
- Four Deputy Governors: Poonam Gupta, M Rageswara Rao; J Swaminathan and T Rabi Shankar.
- First Governor of Reserve Bank of India: Sir Osborne Smith
- First Indian Governor of RBI: Sir C. D. Deshmukh
Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI)
- UIDAI is a statutory authority under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, responding for issuong Aaadhar numbers and regulating related services.
- Established: 28 January 2009
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Chairman: Neelkanth Mishra/ First Director General: Shri Nandan Nilekani
- Chief Executive Officer (CEO): Bhuvnesh Kumar
Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)
- CSIR is India’s largest research and development (R&D) organization.
- Established: 26 September 1942
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Director General: Nallathambi Kalaiselvi (First woman Director General)
- Founder: Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar, Arcot Ramasamy Mudaliar
- First Director General: Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is a key regulator of the securities markets in India. It is formed on 12 April 1988 and was given statutory powers by the Indian government on 30 January 1992, through SEBI Act, 1992. SEBI’s primary goal is to enhance market transparency. Headquarter of SEBI is in Mumbai, SEBI also has regional offices in Kolkata, New Delhi, Ahmedabad, and Chennai.
Ministry : Ministry of Finance, Type: Regulatory Body, First chairman :Dr. S. A. Dave, Current chairman: Tuhin Kanta Pandey

SEBI’s main role is to regulate, monitor, and manage the functioning of the Indian capital market. Its primary aim is to protect investors’ interests and foster a safe investment environment through the implementation of rules and regulations. Moreover, SEBI formulates investment-related guidelines to improve the investment scenario in India.
Bombay Stock Exchange
- Headquarters: Mumbai
- Establishment: 1875
- Founder of BSE- Premchand Poychand
- chairman: Subhash Chaudhary
- MD & CEO: Sundararaman Ramamurthy
- First stock Exchange of Asia: Bombay Stock Exchange
- Name of index of BSE: Sensex
National Stock Exchange (NSE)
- Establishment: 1992
- Headquarters: Mumbai
- MD & CEO: Ashish Kumar Chauhan
- Name of index of NSE: Nifty
- Ferwani Committee recommended the establishment of NSE
Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) is the head of the supreme audit body of India.
- Current Chairman: K Sanjay Murthy
- Establishment: 1858
- Headquarters- New Delhi
- First Chairnan- V. Narhari Rao
- The tenure of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India- 6 years
Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC)
- Headquarters: Trombay, Mumbai (Maharashtra)
- Established: 1954 (Established by Homi Jhangir Bhabha as Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay)
- Director: Vivek Bhasin
Central Vigilance Commission (CVC)
- The main function of CVC of India is to keep an eye on the investigation agencies of the country
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Establishment: 11 February 1964
- Central Vigilance Commissioner of India: A. S. Rajeev
- On recommendation of Santhanam Corruption Prevention Committee the CVC was Established
Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), founded by Dr. Vikram Ambalal Sarabhai in 1969, (Headquarter: Bangalore) is India’s space agency dedicated to developing an indigenous space program. As one of the six largest space agencies globally, ISRO operates an extensive fleet of remote sensing (IRS) and communication (INSAT) satellites. These satellites serve the nation’s needs through a network of centers, offices, and research institutes across India.
ISRO functions as the primary research and development branch of the Department of Space (DoS).
The areas of operation of ISRO include broadcasting, weather forecasting, disaster management, geographic information systems, navigation, cartography, telemedicine, and distance education. The noteworthy achievements of ISRO include Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), Chandrayaan Missions, PSLV and GSLV Launch Vehicles.
Current chairman of ISRO- Dr. V. Narayanan

Some upcoming missions of ISRO are:
Nasa-Isro Synthetic Aperture Radar (Nisar)–
This joint initiative between NASA and ISRO focuses on leveraging sophisticated radar imaging technology to monitor and assess worldwide environmental shifts, encompassing natural calamities and ecosystem alterations.
Gaganyaan–
The Gaganyaan mission scheduled for 2025 represents a historic milestone as it will mark India’s inaugural crewed spaceflight, carrying Indian astronauts into space for the first time. Also, for this Vyommitra, a humanoid robot developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It is set to play a pivotal role in the Gaganyaan mission.
Shukrayaan–
It is an orbiter mission for study of the atmosphere of Venus. Conduct extensive scientific observations.
National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)
- NHAI is an autonomous agency responsible for the development, maintenance and management of national highways in India.
- Established: 1995 (under NHAI Act, 1988)
- Chairman: Santosh Kumar Yadav
Indian Olympic Association (IOA)
- Establishment: 1927
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- President: P. T. Usha (First female President)
- First President if IOA: Sir Dorabji Tata
- India Participated in Olympics for the first time in: 1900 Paris Olympics
- First Indian Athlete to participate in the 1900 Paris Olympics: Norman Pritchard
Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- UPSC is a constitutional body that recruits high level officials for the government of India and advises on appointments.
- Formation: 1 October 1926 (on the recommendation of Lee Commission)
- Establishment:26 October 1950
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Chairman: Ajay Kumar
- First Chairman of UPSC: Sir Boss Barker
- As per Indian Constitution, a member of UPSC can hold the position for: a period of six years or until he attains the age of 65 whever is earlier.
Supreme Court of India
- Establishment: 1 October, 1937 (during British India)
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Supreme Court of independent India established: 28 January 1950
- Chief Justice of India: Justice Bhushan Ramakrishna Gavai
- The Supreme Court (SC) consists of 1 Chief Justice and 33 other judges appointed by the President of India (33+1)
- Every judge of the Supreme Court in India will hold office till he attains the age of 65 years
Also read Union Budget 2025-26 current affairs
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) stands as the primary research and development entity of the Indian government, with its headquarters located in New Delhi. Formed in 1958 through the amalgamation of the Technical Development Establishment (TDEs) of the Indian Army, the Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP), and the Defence Science Organisation (DSO), DRDO holds the responsibility for advancing defence technologies and weapon systems for the Indian armed forces. Additionally, it actively fosters indigenous defence manufacturing and supports exports in the sector.
- DRDO has played a primary role in advancing various defense technologies and systems, encompassing missiles, aircraft, combat vehicles, radars, electronic warfare systems and naval systems.
- DRDO serves as the research and development division of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- Current Chairman DRDO- Samir V Kamat
- First Chairman: Dr. V. R. Rao
- Motto: Balsya Moolam Vigyanam (Strength’s Origin is in Science)
Also read current scenario of Renewable Energy in India
Recent developments:
On 11 March 2024, Narendra Modi, the Prime Minister celebrated the successful completion of Mission Divyastra, marking the inaugural flight test of the Agni-V missile equipped with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology, which was developed in-house.
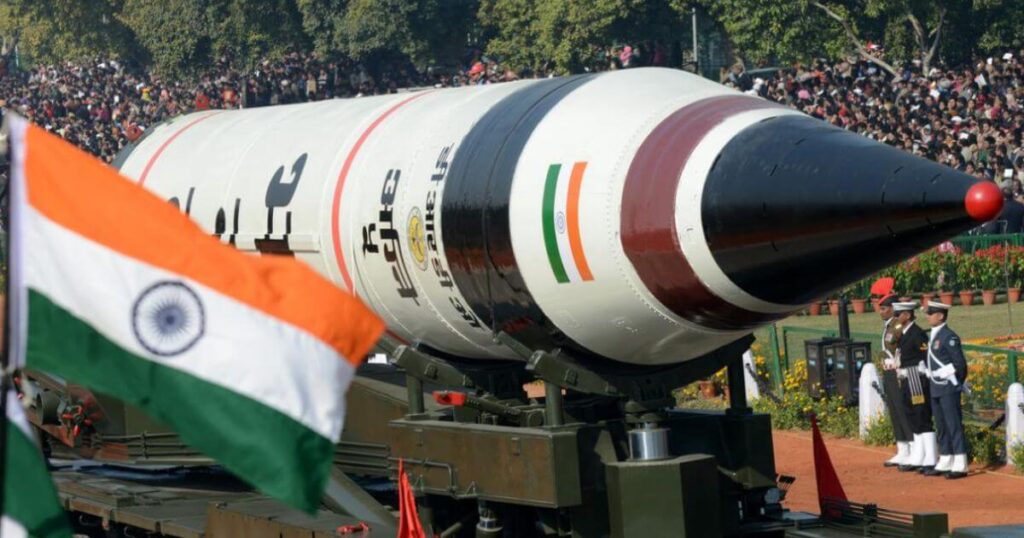

On May 1, 2024, the DRDO effectively conducted a trial of the advanced Supersonic Missile-Assisted Release of Torpedo (SMART) system from Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Island, situated off the Odisha coast.
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Establishment 22 September 1974
- President: Amandeep Garg
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is India’s leading development financial institution, dedicated to offering financial and technical support to the agricultural and rural sectors. Founded on July 12, 1982, NABARD aims to foster sustainable and equitable development in these areas. The headquarter of NABARD is Mumbai and the current chairman of it is Mr. Shaji K. V.
The first chairman: B. Sivaraman. The Associated Ministry is Ministry of Finance.
The main objectives of NABARD:
Promotion of Agriculture and Rural Development, Facilitating Credit for Agriculture, Promoting Rural Infrastructure Development, Promoting Sustainable Agriculture, Institutional Development, Financial Inclusion and Rural Innovation which provides funding and support for rural startups, agri-businesses, and rural artisans to encourage economic diversification and employment generation.
Also read National Parks of India
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)
- TRAI is an autonomous regulatory authority that oversees the telecommunication sector of India.
- Establishment: 20 Febuary 1997
- Headquarters: New delhi
- Chairman: Anil Kumar Lahoti
National Institution for Transforming India (NITI) Aayog
NITI Aayog, the National Institution for Transforming India, is a policy think tank of the Indian government, established to succeed the Planning Commission. Established on January 1, 2015, its purpose is to promote cooperative federalism by engaging state governments in economic policy-making through a bottom-up approach.
Key roles of NITI Aayog includes Policy Development, Coordination and Oversight, Promotion of Innovation and Research, Encouragement of Public-Private Partnerships, State Support etc.
- Chairman: Narendra Modi
- Vice Chairman: Mr. Suman Beri
- First Vice Chairman of NITI Aayog: Arvind Panagariya
- The Governing council of NITI Aayog includes: Prime Minister, all Chief Ministers and Lieutenant Governors
- CEO of NITI Aayog– Shri B.V.R. Subrahmanyam
Also Read:
https://minikosh.com/education-central-schemes-current-affairs-2024-part-2/