Important Indian National Movements-
Explore significant Indian National Movements from 1885 to 1947. Short notes and insights on crucial independence efforts.
Table of Contents
Important Indian National Movements 1885 to 1947| Short notes on Indian National Movement (Part-2)
Dandi March (1930)
On March 1930, Gandhi ji took out a Dandi March from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi.
Mahatma Gandhi broke the salt Law on the beach of Dandi in Gujarat on April 6, 1930.
The Viceroy of India at the time of Gandhiji’s Dandi March was Lord Irwin
The Dandi March was 240 miles (390 kilometers) long.
This march was started by Gandhiji with 78 of his trusted volunteers.
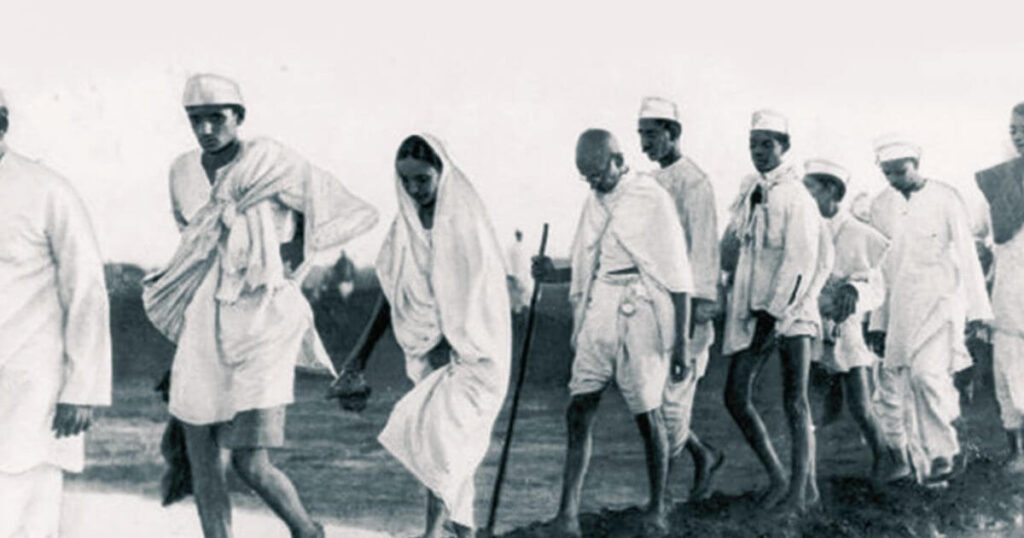

First Round Table Conference (1930-1931)
The First Round Table Conference was held from November 12, 1930 to January 19, 1931 at the Royal Gallery House of Lord of Lords in London. It was inaugurated by George V and chaired by British Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald.
Lord Irwin was the Viceroy of India during the First Round Table Conference.
A total of 74 delegates from India participated in this conference, including 58 political leaders and members of 16 princely states.
The Indian National Congress did not participate in this conference.
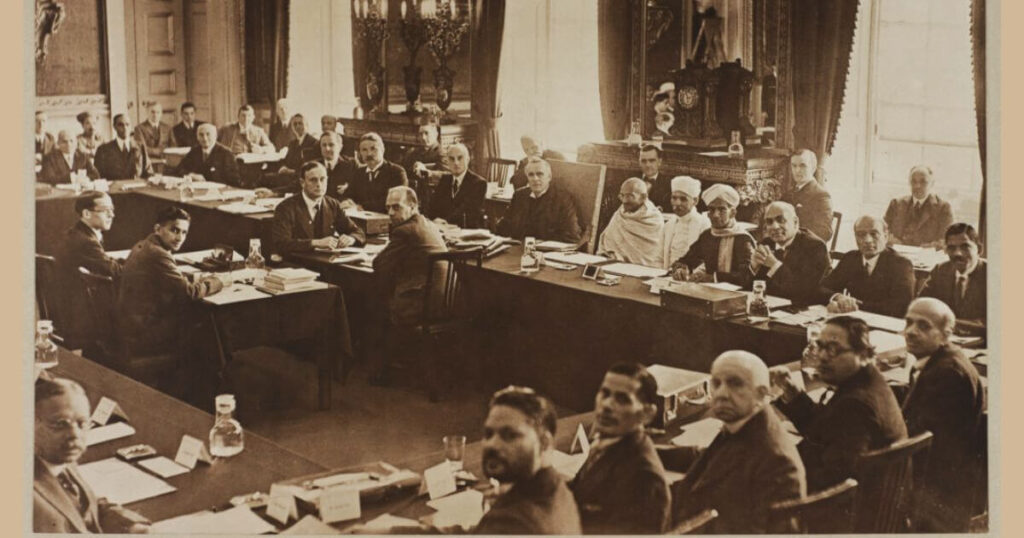

Second Round Table Conference (1931)
The Second Round Table Conference was held in London from September 7, 1931 to December 1, 1931.
In this conference, Mahatma Gandhi represented the Indian National Congress and Sarojini Naidu represented Indian women.
The conference was chaired by the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Ramsay MacDonald.
Poona Pact (1932)
The Poona Pact was an agreement signed between Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar on September 24, 1932.
Under this agreement, the depressed classes were given reservation on electoral seats in the Parliament of British India. The agreement was signed by Madan Mohan Malviya on behalf of Mahatma Gandhi and Dr Ambedkar at Pune’s Yerawada Central Jail.

Third Round Table Conference
The Third Round Table Conference was held in London from November 17, 1932 to December 24, 1932. Only 46 delegates attended the conference.
The Labour Party, Gandhi and the Indian National Congress (INC) did not attend the conference.
Participated in all three round table conferences- Dr. B. R. Ambedkar, Tej Bahadur Sapru, M. R. Jayakar, N. M. Joshi, C. N. Mudaliar
Government of India Act (1935)
The Government of India Act, 1935 was passed by the British Parliament in 1935 and it came into force in 1937.
It was based on the report of the Joint Select Committee led by Lord Linlithgow.
Burma was seperated from India by the Government of India Act, 1935.
The Council of India was abolished by the Government of India Act, 1935.
Muslim League (1940)
The Muslim League demanded a seperate Muslim state i.e. Pakistan in its session held in Lahore in 1940. This resolution is also known as Lahore Resolution or Pakistan Resolution.
On August 16, 1946 declared as ‘Direct Action Day’ by the Muslim League as a means of fulfilling the demand of Pakistan.
Cripps Mission (1942)
The Cripps Mission was sent by the British government in March 1942 with the aim of securing Indian cooperation and support for the British was effort.
Mahatma Gandhi considers Cripps Mission’s proposals as ‘post-dated cheques’
Jawaharlal Nehru and Maulana Azad were the official negotiators of the Cripps Mission.
When Lord Linlithgow was the Viceroy, the Cripps Mission visited India.
The British Prime Minister at the time of Cripps Mission in India was Winston Churchill.
The Quit India Movement was launched in 1942 after the failure of Cripps Mission.
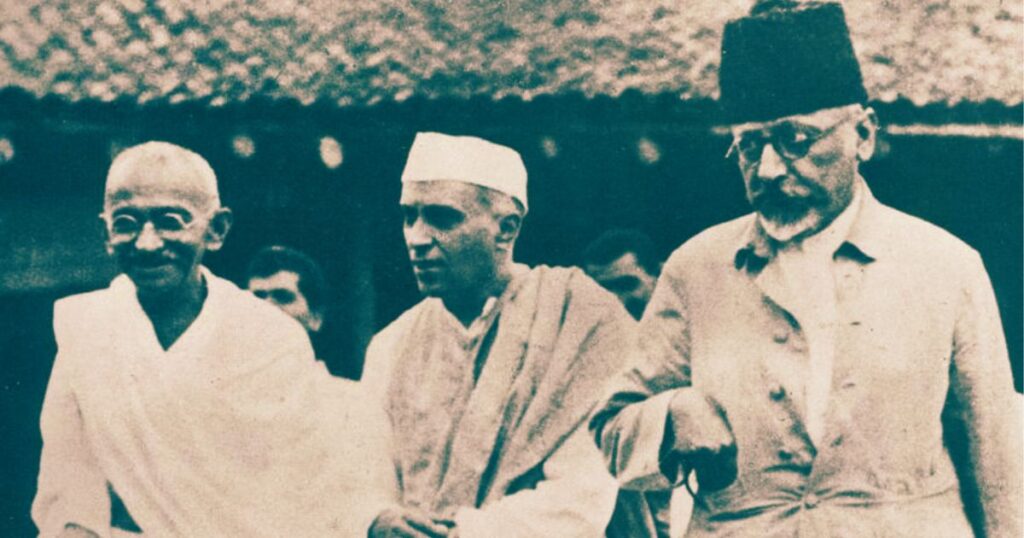

Quit India Movement
The Quit India Movement was proposed by Jawaharlal Nehru.
The Quiz India resolution was passed by Mahatma Gandhi at the All India Congress Committee session at the Gowalia Tank Maidan in Mumbai on August 8, 1942.

The purpose of this proposal was to end British rule in India. This movement is also known as ‘August Movement’ and ‘August Kranti’.
Operation Zero Hour was launched by the British During August Movement.
The slogan ‘Quit India’ was given by Socialist Congress leader Yusuf Meher Ali.
During the Quit India Movement, most of the Congress leaders, including Mahatma Gandhi, were arrested on the morning of August 9, 1942. Gandhiji was detained in the Ahmednagar Fort.
During this movement, Gandhiji gave the slogan of “Do or Die“.
The Quit India Movement was launched by Gandhiji on August 9, 1942 in India during World War II.
Shimla Conference
The Simla Conference was a meeting between Viceroy Lord Wavell and prominent political leaders of British India, in Shimla, India.
A total of 22 delegates participated in the Shimla Conference.
The conference began in Shimla on June 24, 1945 and till July 14, 1945.
The Simla Conference proved to be a failure because the ‘Muslim League’ put a condition that it would select all the Muslim members to be appointed to the Viceroy’s Execution Council.
Cabinet Mission Plan (1946)
The Cabinet Mission came in 1946 to discuss the way the Constitution was framed in India.
Its purpose was to transfer power to India in a peaceful manner and to build a consensus on framing a constitution.
The mission was announced by British Prime Minister Clement Attlee.
On March 24, 1946, three members of the British cabinet- Lord Patrick Lawrence (India Secretary), Sir Stafford Cripps (Chairman of Board of Trade) and A. V. Alexander (Minister of the Navy) came to India.
Indian Independence Act (1947)
The Partition of India was the Partition of British India in 1947, with which Pakistan was also created.
On June 3, 1947, Mountbatten announced the partition of India in a press conference and also declared the date of independence on august 15,1947
The Chairman of India and Pakistan Boundary Commission, declared by Lord Mountbatten in 1947, was Cyril Radcliffe.
Also read Union Budget 2025-26 current affairs
Some important questions
Azad Hind Fauj was formed by?
Ans: Subhash Chandra Bose
(Facts: On October 21, 1943, Subhash Chandra Bose formed the Azad Hind Fauj in Singapore. The idea of the Indian National Army (INA) to liberate India was originally conceived by Rashbehari Bose, who migrated to Japan in 1915.)
‘Poona Public Assembly’ was founded by?
Ans: Mahadev Govind Ranade
(Facts: Poona Sarvajanik Sabha was founded on April 2, 1870 in Pune by Ganesh Vasudev Joshi, S. H. Chiplunkar, and Mahadev Govind Ranade)
Who threw a bomb in the Central Assembly of Delhi in April 1920?
Ans: Sardar Bhagat Singh
(Facts: On April 8, 1929, Bhagat Singh and Batukeshwar Dutt threw bombs in the Central Legislative Assembly in Delhi.
The Central Legislative Assembly Bomb Case (1929) was filed against Batukeshwar Dutt. They started shouting slogans of ‘Inquilab Zindabad‘ from the visitors’ gallery in the Central Assembly Hall.)
When and where was the resolution of ‘complete independence’ passed by the congress?
Ans: Lahore session of Congress, 1929
(Fact: The Indian National Congress passed the resolution of ‘Purna Swaraj‘ i.e. complete independence in its Lahore session on December 19, 1929.
Jawaharlal Nehru was elected President of the Congress in this session. On December 31, 1929, Nehru hoisted the tricolour on the bank of Ravi river and demanded Purna Swaraj.)
Also read current scenario of Renewable Energy in India
Whose statement is ‘Freedom is my birthright and I shall have it’?
Ans: Bal Gangadhar Tilak
(Facts: Tilak is also called the ‘Father of Indian Unrest‘. He belonged to an extremist group. He published two magazines- Kesari in Marathi and Mahratta in English. )
In which session did the militant and liberal leaders of the Congress reconverge?
Ans: Lucknow Session (1916)
(Facts: Ambikacharan Majumdar presided over the Lucknow session of the Indian Nation Congress in 1916.)
In which round table conference did Mahatma Gandhi participate?
Ans: Second
Who was the Governor General of India at the time of ‘Sepoy Mutiny’?
Ans: Lord Canning
(Facts: The Sepoy Mutiny of 1857 began in Meerut on May 10, 1857. This rebellion was started by the soldiers of Bengal Presidency against the rule of the British East India Company. The revolt ended in Gwalior on June 20, 1858.)
Which party was founded by Subhash Chandra Bose after leaving the Congress in 1939?
Ans:Forward Bloc
(Fact: The All India Forward Bloc (AIFB) is a left- wing nationalist political party founded in 1939 by Subhas Chandra Bose in West Bengal.)
When was the Gandhi-Irwin pact signed?
Ans: 5 March 1931
(Facts: The Gandhi-Irwin pact was related to India’s Civil Disobedience Movement. The agreement was signed by Mahatma Gandhi and Lord Irwin on March 5, 1931. According to the Gandhi-Irwin Pact, Gandhi suspended the Civil Disobedience Movement and agreed to participated in the Second Round Table Conference.)
According to Dr. Rajendra Prasad, who was the father of Pakistan?
Ans: Lord Minto
Under whose rule was the ‘Vernacular Press Act’ passed?
Ans: Lord Lytton
Who propounded the two- nation theory?
Ans: Mohammad Ali Jinnah
(Facts: The two- nation theory is considered to be the real father of Sir Syed Ahmed Khan. However, in the early 20th century, Pakistan’s founder Mohammad Ali Jinnah also proposed this theory.)
Who founded the ‘Deccan Education Society’?
Ans: Bal Gangadhar Tilak and Gopal Ganesh Agarkar (in the year 1884 in Pune.)
When was the first Independence Day celebrated all over India?
Ans: Jan 26, 1930
Which institution was established by revolutionary leaders in Bengal?
Ans: Anushilan Samiti
Indian National Movements 1985-1947 (Part-1)