Explore the latest developments in renewable energy in India for 2025. Stay updated with sustainable energy news and discover the largest renewable energy plants.
Table of Contents
Renewable Energy Current Scenario
Objective
In recent years, the Government of India has accelerated its efforts to meet ambitious clean energy goals, the objective is to bring 50% of the country’s cumulative installed power generation capacity to come from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030 and achieving net zero emissions by 2070.
As per budget 2024-25
FY 2024-25 budget, sustainable financing to support sustainable energy growth is likely to prioritize areas such as distributed renewable energy installations and the localization of the supply chain.
Accelerating rooftop solar installations is expected to receive a significant increase in budgetary allocations, particularly in light of the recent announcement of a 23% increase in per kW central financial assistance for installations up to 3 kW under Phase-II of the Rooftop Solar Scheme.
Subsidies provided under Government of India schemes such as the PM-KUSUM scheme and bio energy program are crucial for enhancing the commercial viability of renewable energy projects. These subsidies facilitate the off-take, financing, and implementation of these projects, making them more attractive to investors and developers.
As per new budget 2025-26
However in FY 2025-26 budget, it does not completely overlook renewable energy, its main emphasis is now on boosting domestic manufacturing instead of expanding renewable energy capacity aggressively. A National Manufacturing Mission has been introduced to promote the local production of solar PV cells, EV batteries, wind turbines, and grid-scale batteries. This is crucial for the clean energy transition, as these technologies depend on key minerals, and ensuring a stable and reliable domestic supply chain will be essential moving forward.
To support this shift, the Budget includes customs duty exemptions on 35 capital goods related to EV battery production and 28 for mobile phone batteries. It also reduces the import duties on solar modules from 40% to 20%, making it less expensive to bring in components for solar projects.
However, this change contrasts with the government’s earlier approach of encouraging domestic solar manufacturing by imposing high import tariffs. The impact of these changes on the existing Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes for Solar PV and Advanced Chemistry Cells (ACC) in India will need to be carefully evaluated.
Additionally, green hydrogen and electrolyser production are key priorities. The government intends to promote electrolyser manufacturing through policy support, with the goal of positioning India as a leader in hydrogen technology. However, hydrogen technology is still in its early stages globally, and its widespread adoption is likely several years away. The National Hydrogen Mission, which was previously announced, depends on green energy to produce green hydrogen. A shift towards nuclear energy might also necessitate rethinking the standards for green hydrogen, potentially categorizing hydrogen derived from nuclear-powered electricity as “pink hydrogen.”
Also read :
Central government scheme PM-KUSUM and other schemes
Pradhan Mantri Surya Ghar Free Electricity Scheme and other schemes
As of Jan 2025, the total installed capacity of renewable energy sources including large hydropower is 209.44 GW. The capacities for specific renewable energy sources are:
- Solar Power: 97.86 GW
- Wind Power: 48.16 GW
- Biomass/Co-generation: 11.35 GW
- Small Hydro Power: 5.10 GW
- Waste to Energy: 0.59 GW
- Large Hydro: 46.93 GW
India’s objective is to reduce the carbon intensity of its economy by under 45% by 2030, achieve 50% of its cumulative electric power from renewables by 2030, and reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2070. India is also aiming to have 500 GW of renewable energy installed capacity by 2030.
Solar Plants
Solar technologies transform sunlight into electrical energy using either photovoltaic (PV) panels or mirrors that focus solar radiation. This energy can then be used to produce electricity or stored in batteries or thermal storage systems for future use.
Top Solar Plants in India
India’s largest Solar Plant
The Bhadla Solar Park, spread across 56 square kilometers in Rajasthan, India, secured the titles in 2023 for being both the largest solar power plant in India and globally, boasting a capacity of 2,245 MW. Established through four phases starting in 2015, it has gathered funding from diverse channels, playing an essential role in India’s sustainable energy aspirations while curbing annual greenhouse gas emissions by a notable 4 million tons.
Second Largest Solar Plant-
Pavadaga Solar Park, located in Karnataka’s Tumkur district, covers an area of 53 square kilometers, positioning it as the second-largest solar power facility in India and the third-largest globally, boasting a capacity of 2050 MW. Constructed in 2019 at an investment of Rs.14,800 crores, it holds the distinction of being India’s second-largest solar park.
Third Largest Solar Plant-
The Ananthapuramu Ultra Mega Solar Park, positioned as the third largest solar power plant, sprawls across the Anantapur district of Andhra Pradesh. Covering a vast expanse of 32.07 square kilometers, it holds the distinction of being India’s third-largest solar park, closely trailing behind the Golmud Solar Park in China and the Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan, as well as the Pavagada Solar Park in Karnataka.
Fourth Largest Solar Plant-
Kurnool Ultra Mega Solar Park
Location: Andhra Pradesh
Power Generation: 1000 MW
Area of Park:5932 acres
Fifth Largest solar plant-
NP Kunta Ultra Mega Solar Park
Location: Andhra Pradesh
Power Generation: 978 MW
Area of Park:7924 acres
Sixth Largest solar plant-
Rewa Ultra Mega Solar Plant
Location: Madhya Pradesh
Power Generation: 750 MW
Area of Park: 1590 acres
Seventh Largest solar plant-
Kamuthi Solar Power Project
Location: Tamil Nadu
Power Generation: 648 MW
Area of Park: 10 sq. km
Eighth Largest solar plant-
Mandsaur Solar Park
Location: Madhya Pradesh
Power Generation: 600 MW
Area of Park: 2 sq. km
Ninth Largest solar plant-
Ninth Largest solar plant: Bhadla Phase-II
Location: Rajasthan
Power Generation: 500 MW
Area of Park: 4400 acres
Tenth Largest solar plant-
Charanka Solar Park
Location: Gujarat
Power Generation: 500 MW
Area of Park: 20 sq. km
Also read AI current affairs 2025
Wind Farm/Wind power plants
A wind farm, also known as a wind park, wind power station, or wind power plant, consists of a collection of wind turbines situated in one area to generate electricity. The size of wind farms can range from just a few turbines to several hundred, spread over a large area.
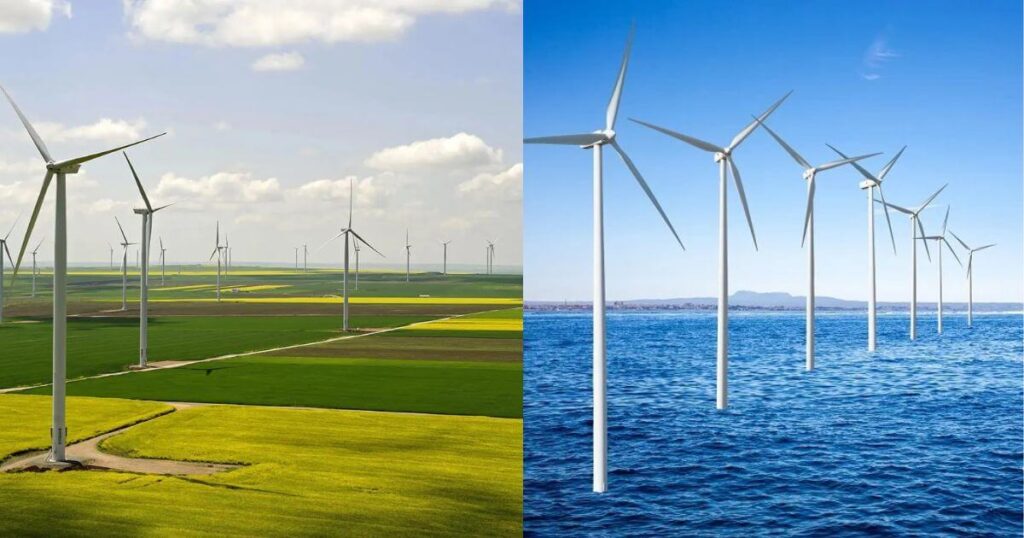

Types of Wind Farms/Parks
- Onshore: These wind turbines are placed on land and use the energy of moving air to produce electricity.
- Offshore: These turbines are positioned in the sea or in freshwater bodies.
Largest Wind Power Plants in India
| S. No. | Wind Power Plant | Location | Megawatt (MW) |
| 1 | Muppandal wind farm | Tamil Nadu, Kanyakumari | 1500 |
| 2 | Jaisalmer Wind Park | Rajasthan, Jaisalmer | 1064 |
| 3 | Brahmanvel wind fard | Maharashtra, Dhule | 528 |
| 4 | Dhalgaon wind farm | Maharashtra, Sangli | 278 |
| 5 | Vankusawade wind park | Maharashtra, Satara District | 259 |
| 6 | Vaspet | Maharashtra, vaspet | 144 |
| 7 | Tuljapur | Maharashtra, Osmanabad | 126 |
| 8 | Beluguppa wind park | Beluguppa, Andhra Pradesh | 100.8 |
| 9 | Mamatkheda wind park | Madhya Pradesh, Mamatkheda | 100.5 |
| 10 | Anantapur wind park | Andhra Pradesh, Nimbagallu | 100 |
In a recent interview with PTI, Union Power and Renewable Energy Minister RK Singh mentioned that the current installed renewable energy capacity is around 190 GW, with an additional 103 GW under construction, a total of 290 GW. Also, 72 GW is under bids, which brings the total to around 360 GW. In this way, India is ready to achieve the target of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030 ahead of schedule.
Leading States in Renewable Energy
Gujarat and Rajasthan boast the largest renewable energy capacities at 29.98 GW and 29.52 GW respectively. They are followed by Tamil Nadu with 23.70 GW, Karnataka with 22.37 GW, and Maharashtra with 17.385 GW. Additionally, Himachal Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh each have an installed renewable energy capacity of 11 GW.
Also visit:
https://minikosh.com/education-important-schemes-2024-part-5/
https://minikosh.com/education-central-government-schemes-2024-part-3/